What is Linked List
- A linked list is a data structure that represents a sequence of nodes.
-
In a singly linked list. each node points to the next node in the linked list.
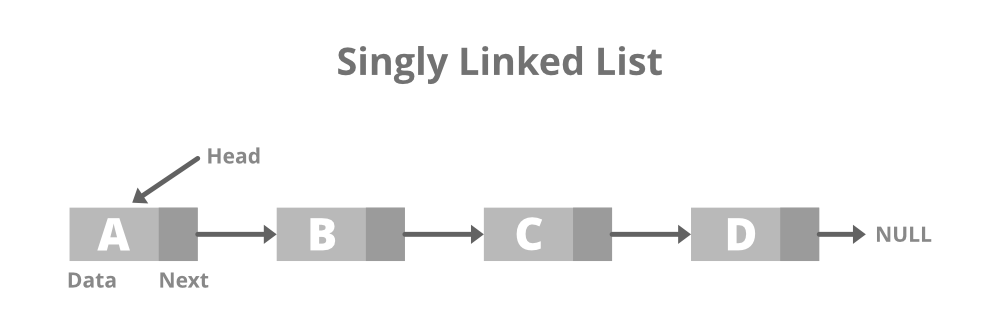
-
A doubly linked list gives each node pointers to both the next node and the previous node.
-
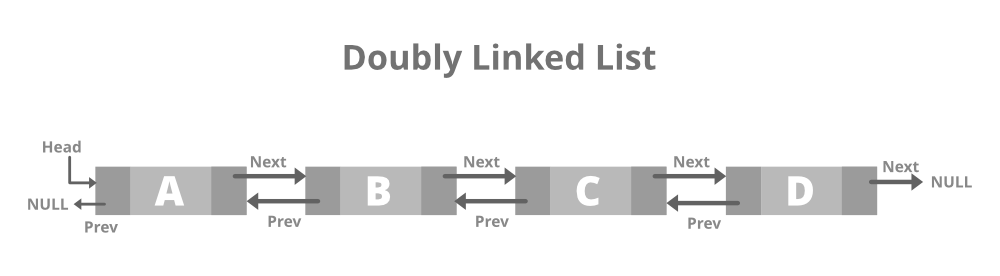
- Unlike an array, a linked list does not provide constant time access to a particular "index" within the list.
- This means that if you'd like to find the Kth element in the list, you will need to iterate through K elements.
- The benefit of a linked list is that you can add and remove items from the beginning of the list in constant time. For specific applications, this can be useful.
The Runner Technique
- aka fast/slow pointers
- aka
floyd's tortoise and hare
- aka
- The "runner" (or second pointer) technique is used in many linked list problems.
- The runner technique means that you iterate through the linked list with two pointers simultaneously, with one ahead of the other.
- The "fast" node might be ahead by a fixed amount, or it might be hopping multiple nodes for each one node that the "slow" node iterates through.
#example finding a middle node in linked-list
def middleNode(head):
slow, fast = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
Tips on Linked List
- In python and other object is pass by reference
- Thus when you copy object the changes will be reflected on the original
- Usually you don’t want this, thus you need to shallow copy such as
- newNode = Node(oldNode.value)